Troubleshooting a circuit:
- 1. Measure the Vce.
- 2. When troubles come, they are usually big troubles like shorts or opens.
- 3. Short: when devices damaged, solder splashes across resistors.
- 4. Open: when components burn out.
- 5. These troubles produce large changes in voltages and currents
Cause of these troubles:
1. Trouble in the power supply
2. An open lead between the power supply and the collector resistor
3. An open collector resistor and so on.
4. Open base resistor
| Trouble | VB, V | VC,V | Remarks |
| None | 0.7 | 12 | No trouble |
| RBS | 15 | 15 | Transistor Blown |
| RBO | 0 | 15 | No Base or Collector Current |
| RCS | 0.7 | 15 | Check RC and Supply connection |
| RCO | 0.7 | 0 | “ |
| No VBB | 0 | 15 | Check supply and lead |
| No VCC | 0.7 | 0 | “ |
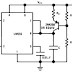
For Example:
If VBB=15V, RB=470kohm, RC=1k ohm, VCC=15 V, current gain= 100
We assume ideal condition. Suppose RB= 1 M ohm, then base current would be 15 uA. Here RB is 470 k ohm nearly half of the 1M ohm. Hence base current would be double, i.e 30 uA. And current gain is 100. So collector current would be 3 mA. When it flows through 1 kohm resistor, it produces a voltage drop of 3 V. So, VCE would be 12 V, or else there is something wrong in this circuit.



 14:09
14:09
 DAS
DAS


 Posted in:
Posted in: 





0 comments:
Post a Comment