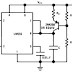
Block diagram for the 555 timer is given in fig.
Working:
In most applications, the control pin is not used, so that the control voltage equals +2Vcc/3 .
Output of comparator 1 is applied to set (S) input of the flip-flop. Whenever the threshold voltage exceeds the control voltage, comparator 1 will set the flip-flop and its output is high. A high output from the flip-flop saturates the discharge ttransistor and discharge the capacitor connected externally to pin 7. The complementary signal out of the flip-flop goes to pin 3, the oputput. The output available at pin 3 is low. Even if the voltage at the threshold input falls below +2Vcc/3, comparator 1 cannot cause the flip-flop to change again. It means that the comparator 1 can only force the flip-flop's output high.
To change the output of flip-flop to low, the voltage at the trigger input must fallbelow +Vcc/3. When this occurs, comparator 2 triggers the flip-flop, forcing its output low. The low output from the flip-flop turns the discharge transistor off and forces the power amplifier to output a high.
Note: When control input is not in use, a 0.01 uF capacitor should be connected between pin 5 and ground to prevent noise coupled onto this pin from causing false triggering.
Main Parts of 555 Timer:
- Two comparators (simply Op-Amp)
- An R-S Flip-flop
- Two Transistors
- A Resistive networks consisting three equal resistors and acts as a voltage divider
Working:
In most applications, the control pin is not used, so that the control voltage equals +2Vcc/3 .
Output of comparator 1 is applied to set (S) input of the flip-flop. Whenever the threshold voltage exceeds the control voltage, comparator 1 will set the flip-flop and its output is high. A high output from the flip-flop saturates the discharge ttransistor and discharge the capacitor connected externally to pin 7. The complementary signal out of the flip-flop goes to pin 3, the oputput. The output available at pin 3 is low. Even if the voltage at the threshold input falls below +2Vcc/3, comparator 1 cannot cause the flip-flop to change again. It means that the comparator 1 can only force the flip-flop's output high.
To change the output of flip-flop to low, the voltage at the trigger input must fallbelow +Vcc/3. When this occurs, comparator 2 triggers the flip-flop, forcing its output low. The low output from the flip-flop turns the discharge transistor off and forces the power amplifier to output a high.
Note: When control input is not in use, a 0.01 uF capacitor should be connected between pin 5 and ground to prevent noise coupled onto this pin from causing false triggering.



 11:15
11:15
 DAS
DAS


 Posted in:
Posted in: 





0 comments:
Post a Comment