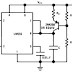
Few Points:
- Two batteries vBB and VCC used
- VBB gives potential to base terminal through RB.
- VCC supplies power to the collector through RC.
- Base resistance RB of the order of hundred kilo ohm
- Collector resistance RC of the order of kilo ohm.
For this purpose, we are going to convert above circuit in electrical equivalent circuit. For making calculation easy, we divide this circuit in two part, (i) Input Part and (ii) Output Part
(I) Input Part:
Applying KVL:
We get, VBB = IBRB + VBE
Or IB = ( VBB – VBE )/ RB
For Silicon Transistor, VBE = 0.7 V and For Ge Transistor, VBE = 0.3 V
(ii) Output Part:
Applying KVL again,
VCE = VCC – IC RC
We know that, IC = β IB
Stability Factor (S) = ( 1 + β )/(1 – β d IB / d IC)
And in fixed biased, IB is independent of IC.
Hence, S = ( 1+ β )
It means collector current (IC) increases ( 1 + β ) times as much as ICO .



 11:34
11:34
 DAS
DAS




 Posted in:
Posted in: 





0 comments:
Post a Comment